Key Features
Allows customers to transform external payment formats to and from the internal data model. The solution provides a set of pre-delivered formats out of the box. Others can be added during implementation leveraging the format converter framework of the solution.
Enhances the payment orders when necessary, through enrichment functions and validates the payment orders against various master data such as the Service Level Agreement and the accounting system of the bank. Country and/or customer specific validations and enrichment functions can be easily added to the process. Enrichments and validations can be carried out for:
-
Payment Order
-
Ordering Party Items
-
Recipient Party Items
-
Cross-Item
Using flexible rule sets rioting identifies the account management system to which an internal payment shall be applied and for external payments how to forward the transaction to another bank or clearing system. The found route and clearing agreement states all the details used in clearing and settlement and how the payment should be forwarded.
Distributes payments internally to account management system(s) and externally to outgoing clearing channels based on the information found in routing control. In clearing and settlement, payments can be batched for a collective posting, queued or posted as single transactions directly.
The central process control manages the end-to-end straight-through processing of payment orders. Payment order processing uses a comprehensive status management to monitor and control the payment processing flow in the solution. Through payment product configuration the process can be easily influenced without any coding or change to the system. For example, payment order processing enables the prioritization of the processing.
At multiple stages within the payment processing, exceptions can be raised due to business rules or other failures. In exception handling customers can configure the possible system responses to exceptions that occur during the end-to-end payment order processing. This function offers a very flexible rule set for differentiating the reaction to different exceptions. Examples of reactions to error situations are manual repair, return or reject.
Key Features
Allows customers to transform external payment formats to and from the internal data model. The solution provides a set of pre-delivered formats out of the box. Others can be added during implementation leveraging the format converter framework of the solution.
Enhances the payment orders when necessary, through enrichment functions and validates the payment orders against various master data such as the Service Level Agreement and the accounting system of the bank. Country and/or customer specific validations and enrichment functions can be easily added to the process. Enrichments and validations can be carried out for:
-
Payment Order
-
Ordering Party Items
-
Recipient Party Items
-
Cross-Item
Using flexible rule sets rioting identifies the account management system to which an internal payment shall be applied and for external payments how to forward the transaction to another bank or clearing system. The found route and clearing agreement states all the details used in clearing and settlement and how the payment should be forwarded.
Distributes payments internally to account management system(s) and externally to outgoing clearing channels based on the information found in routing control. In clearing and settlement, payments can be batched for a collective posting, queued or posted as single transactions directly.
The central process control manages the end-to-end straight-through processing of payment orders. Payment order processing uses a comprehensive status management to monitor and control the payment processing flow in the solution. Through payment product configuration the process can be easily influenced without any coding or change to the system. For example, payment order processing enables the prioritization of the processing.
At multiple stages within the payment processing, exceptions can be raised due to business rules or other failures. In exception handling customers can configure the possible system responses to exceptions that occur during the end-to-end payment order processing. This function offers a very flexible rule set for differentiating the reaction to different exceptions. Examples of reactions to error situations are manual repair, return or reject.
Banking and Payment Solution
SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization is a single-payment operations platform that can connect to multiple internal and external payment channels. You use this component to verify, sort, and clear payment transactions. Its transparent, flexible and automated workflow can be controlled by expert users. SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization provides high straight-through processing rates, batch processing, and real-time processing, as well as 24×7 reporting. It handles low-value, non-time-critical payments as well as high-value, time-critical payments and also allows financial institutions to offer value added real-time services with no interruption from end-of-day processes. It can be co-deployed directly as an add-on to SAP S/4HANA or it can be installed as a standalone version on a single instance of SAP S/4HANA foundation and, if desired, run in a side-by-side scenario with another instance containing SAP S/4HANA. It is based on the SAP HANA database and, as such, offers and makes use of SAP HANA capabilities. Modern user interfaces support users within the bank in different roles to do their daily business as comfortably and smoothly as possible.

SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization supports business models that enable financial institutions and service providers to offer payment processing to in-house entities as well as to external financial institutions, for example, by establishing a shared service center. In the effort towards standardization or during mergers and acquisitions, SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization can be a viable solution for consolidating legacy systems and can provide compliance with future clearing systems, for instance, in preparation for the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA). In the context of international payments, SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization also supports conversion and processing of SWIFT MT103+ messages (Single Customer Credit Transfer), for which it provides full straight-through processing (STP).
Thanks to its parallel-processing capability and its scalability, SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization can handle the high volumes of payments typical of large financial institutions and IT service centers, while allowing institutions with lower volumes to achieve a low total cost of ownership.

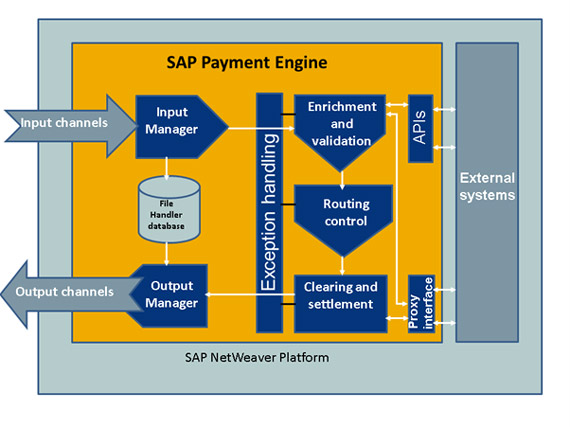
SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization is a standalone product with the means of connecting banking services over the SAP NetWeaver platform. You can connect account-management systems through a proxy infrastructure and other external tools and applications, such as embargo, anti-money-laundering, or reporting systems, by implementing Business Add-Ins (BAdIs), the standard technology for customer extensions. You can archive payment transactions and other relevant data using the Archiving Engine.
The figure below shows a basic landscape example of SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization and the flow of payment information.
Banking and Payment Solution
SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization is a single-payment operations platform that can connect to multiple internal and external payment channels. You use this component to verify, sort, and clear payment transactions. Its transparent, flexible and automated workflow can be controlled by expert users. SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization provides high straight-through processing rates, batch processing, and real-time processing, as well as 24×7 reporting. It handles low-value, non-time-critical payments as well as high-value, time-critical payments and also allows financial institutions to offer value added real-time services with no interruption from end-of-day processes. It can be co-deployed directly as an add-on to SAP S/4HANA or it can be installed as a standalone version on a single instance of SAP S/4HANA foundation and, if desired, run in a side-by-side scenario with another instance containing SAP S/4HANA. It is based on the SAP HANA database and, as such, offers and makes use of SAP HANA capabilities. Modern user interfaces support users within the bank in different roles to do their daily business as comfortably and smoothly as possible.

SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization supports business models that enable financial institutions and service providers to offer payment processing to in-house entities as well as to external financial institutions, for example, by establishing a shared service center. In the effort towards standardization or during mergers and acquisitions, SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization can be a viable solution for consolidating legacy systems and can provide compliance with future clearing systems, for instance, in preparation for the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA). In the context of international payments, SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization also supports conversion and processing of SWIFT MT103+ messages (Single Customer Credit Transfer), for which it provides full straight-through processing (STP).
Thanks to its parallel-processing capability and its scalability, SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization can handle the high volumes of payments typical of large financial institutions and IT service centers, while allowing institutions with lower volumes to achieve a low total cost of ownership.

SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization is a standalone product with the means of connecting banking services over the SAP NetWeaver platform. You can connect account-management systems through a proxy infrastructure and other external tools and applications, such as embargo, anti-money-laundering, or reporting systems, by implementing Business Add-Ins (BAdIs), the standard technology for customer extensions. You can archive payment transactions and other relevant data using the Archiving Engine.
The figure below shows a basic landscape example of SAP S/4HANA Banking for payment centralization and the flow of payment information.